Ferguson Lab

The Ferguson lab aims to understand the molecular and circuit-specific mechanisms that underlie neuropsychiatric disorders. Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a leading cause of disability, with ~20% of individuals suffering from clinical depression during their lifetime.
Depression is a heterogeneous syndrome consisting of several subtypes and abnormalities in multiple brain regions. Despite the prevalence of depression and its considerable impact, knowledge about its pathophysiology is limited.
The Ferguson lab has developed several leading-edge technical approaches to elegantly dissect the cell and circuit-specific mechanisms of depression including cell- type specific RNA-Seq, cell and circuit-specific optogenetic approaches, epigenetic remodeling using CRISPR/Cas9, operant measures of reward, single- cell RNA-seq and the establishment of 19 unique transgenic lines. Using these cutting-edge molecular and circuit approaches, the Ferguson lab aims to develop better diagnostic tests, treatments, and preventive measures for depression.
Depression is a heterogeneous syndrome consisting of several subtypes and abnormalities in multiple brain regions. Despite the prevalence of depression and its considerable impact, knowledge about its pathophysiology is limited.
The Ferguson lab has developed several leading-edge technical approaches to elegantly dissect the cell and circuit-specific mechanisms of depression including cell- type specific RNA-Seq, cell and circuit-specific optogenetic approaches, epigenetic remodeling using CRISPR/Cas9, operant measures of reward, single- cell RNA-seq and the establishment of 19 unique transgenic lines. Using these cutting-edge molecular and circuit approaches, the Ferguson lab aims to develop better diagnostic tests, treatments, and preventive measures for depression.
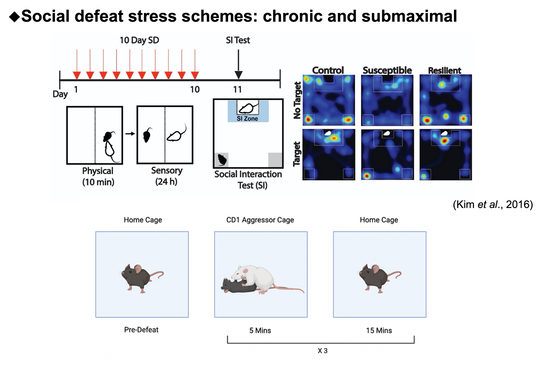
Project 3. Cell-Type Specific RNA-Sequencing
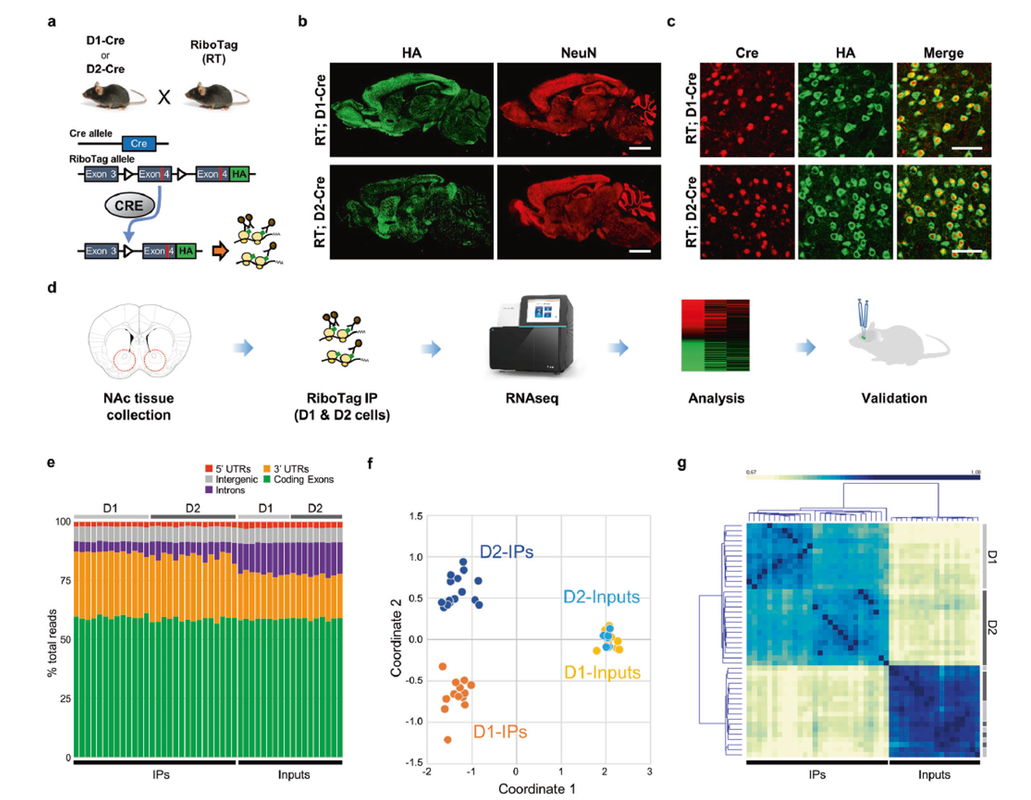
MSN subtype specific transcriptomics in the Nucleus Accubens. a Schematic diagram of RT; D1-Cre and RT; D2-Cre mice generation and purification of MSN-subtype specific transcripts. The exogenous exon 4-HA cassette is expressed when the floxed exon 4 is excised in Cre-expressing cells. The HA-tagged polyribosome allows cell-type specific mRNA preparation from D1-MSNs (RT; D1-Cre) or D2-MSNs (RT; D2-Cre). b, c Validation of RiboTag mice with immunohistochemistry across brain regions (sagittal; scale bar, 2 mm) (b) and in the NAc (coronal; scale bar, 50 μm) sections (c). d Schematic diagram of experimental design. e Read mapping composition of each RNA-seq sample on the mouse genome, mm10 (% average for coding regions: IPs, 59.2% vs inputs, 58.8%; for intronic regions: IPs, 5.5% vs inputs, 13.4%). f Clustering of RNA-seq samples of RT; D1- and D2-Cre in a MDS plot. g Sample correlation heatmap were plotted with clustering (The dendrogram annotations on the right side axis: D1, light gray; D2, dark gray).